
Knee
Information about knee rehabilitation after surgery
Knee rehabilitation starts after the patient is discharged from the clinic or hospital where they had their knee operation.
During the post-operative knee rehabilitation period it is important to do rehabilitation exercises in which full and gradual rehabilitation depends largely on the patient's persistence and continuity with the exercise programme.
Rehabilitation Treatment
- A drainage massage is administered and the patient is shown how to place the affected limb.
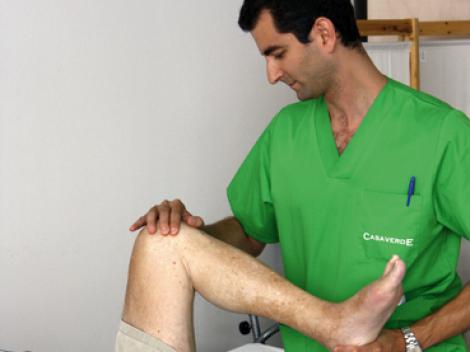
- Mobility exercises are carried out on the kneecap.
- Patients are shown static isometric exercises for the quads and hamstrings Tibialis and peroneus muscles. Calf muscles.
- Electro-analgesic treatment is applied. Ultrasound - anti-inflammatory drugs - tissue repair metabolism activators. Thermotherapy - Cryotherapy. (Measures intended to improve the articulation and muscle tone around the knee prosthesis).
- Assisted mobilisation of the knee is done manually at first, gradually increasing the degree of flexion the replacement knee joint.
- Mechanical equipment such as the Artromotor or Kinetec may be used to aid knee flexion and extension At first, the knee should not be bent any further than 60º, with the range being increased gradually.
- Muscular electro-stimulation may be applied to muscle groups that have been weakened following the operation, with special easy-to-use electrical stimulators.
- The affected leg will be raised in a straight position so that the knee can be fully extended and the muscles around the pelvic and abdominal area can be strengthened.
- Showing patients how to move from the trolley, to a chair and into bed Restoring patients' confidence when moving their lower limbs.
- Patients are shown how to stand correctly, with support for the leg on the affected side, spreading their weight, and they are also shown how to do load-bearing exercises. This is usually done facing a mirror so the patient can improve control over their posture when standing upright.
- Patients are given exercises to tone the pelvis and trunk to make standing upright easier and give them increased body control before starting walking exercises.
- Walking exercises using parallel bars, assisted walking using crutches, walking up and down ramps and stairs.
- Exercises to improve proprioception in lower limbs Practising changing direction, avoiding obstacles, changing surfaces.
- If the operation wound has healed and the patient is given the go-ahead to use the pool: Aqua-walking in the hydrotherapy pool to build strength and confidence for walking independently without walking aids.
- Patients are given guidance on how to look after their knee replacement and prevent undesired complications Patients are advised to avoid jumping with all their weight on the affected knee. They must not make forced movements with the replacement knee and avoid any sudden turning or twisting movement to the knee joint.
Maintenance and Practical Advice
- They should get up from an armchair and sit down using both arms, as well as try to avoid inclines and stairs, or at least use them with caution.
- Patients should not crouch down or kneel.
- They should also watch their weight.
- For 4 to 6 months after the operation, twice a week: resistance exercises may be done with weights (if there any problems with the upper leg joint, pulley weights should not be used).
- Then every year: Isometric exercises for the four muscle groups and proprioceptive retraining.
The Importance of Immediate rehabilitation
- Thorough rehabilitation is essential following an operation of this kind. Rehabilitation should start as soon as possible and patients should try to avoid travelling, making sudden movements or lifting heavy objects in the first few days. Before patients return to their home country, we advise them to undertake at least 8 days of rehabilitation at our Casaverde rehabilitation centre.
- An early start enables muscle tone to be improved; muscles around the affected area become gradually stronger and more powerful as they are worked consistently during treatment. Strong muscles reduce the risk of falls and complications.
- Early rehabilitation leads to a faster recovery of movement in the affected joint and reduces the pain and/or soreness that may develop following an operation.
- Early rehabilitation improves trophism (nourishment of the tissues surrounding the surgery site) and encourages the wound to heal correctly.
- Rehabilitation enables mobility to be recovered faster, enabling patients to walk again with the assistance and guidance of the care team as they learn to re-programme their walking patterns.



